Learn Echocardiography | Standard Protocol for Performing Comprehensive Echocardiogram | Explained with Images and Videos
If you are just starting to learn echocardiography, you will find that learning the full echo examination protocol will be immensely useful. The full protocol will provide a solid foundation for your career in echo. I personally found that once I could execute the standard protocol flawlessly, I was able to add and refine additional echo scanning skills while deepening my understanding of the purpose of each echo image. The echo protocol illustrated in this article is the same one we currently use for all our patients in the hospital and meets or exceeds the standards of American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) for an adult echocardiography examination. The protocol presented here is meant as a guideline and does not cover every aspect (such as off axis views) of an echo examination. Also other hospitals will probably have slight variations of this protocol depending on the lab's needs, which is normal. This article's main purpose is to provide a solid foundation for the beginning cardiac sonographer/student to build on.
- Correct probe positioning
- Standard Echo Protocol
- Labeling of Key Images
- Video of a Complete Echo Examination
✅ Visit ECHO Library to practice 100 plus Echocardiography Cases
1. How to Obtain Key views | Probe Positioning:
Parasternal Long Axis (PLAX):
Left 4th ICS - Pointer towards right shoulder
Parasternal RV Inflow:
From PLAX tilt tail down towards left shoulder directing towards patient’s right hip
Parasternal RV outflow:
Angling beam towards left shoulder (tail away from left shoulder)
Parasternal Short Axis (PSAX):
From PLAX, rotate pointer towards left shoulder, move towards base or apex to get different levels (Aortic, Mitral and Mid LV cavity level)
Apical Four chamber(A4C):
Probe at apex, pointer towards appendix (LV appears on left side of screen)
(many centers keep pointer at 3 O' clock position so that LV appears on right side of the screen)
Apical Three chamber (A3C):
From A4C rotate towards right shoulder
Apical Two Chamber (A2C)
From A3C rotate towards left shoulder
Subcostal:
Subcostal 4 chamber: Probe at epigastrium, pointer at 3 O’ clock, tilt probe anteriorly, move beam in between suprasternal notch and left clavicle
For IVC: rotate pointer anticlockwise to about 12 o clock, then tilt probe superiorly with beam directed thru the abdomen, adjust beam slightly towards IVC (right lateral)
For Abdominal aorta: angle the beam towards left side (left lateral)
Suprasternal:
Probe at suprasternal notch, pointer towards chin
2. Standard Echo Protocol:
Parasternal Long Axis (PLAX):
- 2D image with increased depth
- 2D image with decreased depth
- Color Doppler on AV, MV, IVS
- M- Mode on Left ventricular level, MV and Aortic root
- Measure IVS, LVID and PWT in diastole and systole at MV tip level
- Measure Proximal RVOT
- Zoom LVOT, measure LVOT diameter, AV annulus
- Zoom, color Doppler on Aortic Root, measure at Sinus of Valsalva, SinoTubular Junction and at ascending aorta level
- LA diameter in 2D image
RV Inflow View:
- 2D Image
- Color on TV
- CW on TV
RV outflow View:
- 2D Image
- Color on pulmonary valve
- CW on Pulmonary Valve
Parasternal Short Axis (PSAX)
At the level of great vessels- For branches of pulmonary artery
- 2D image
- Zoom/Focus on TV
- Color on TV
- CW on TV
- Zoom/Focus on PV
- Color on PV
- CW on PV
- Zoom image of LA Appendage
- 2D Image
- Color on MV
- 2D image
Apical Four Chamber View:
- 2D Image
- Zoom at Ventricular level
- Zoom/Focus on MV
- Color on MV
- CW on MV
- PW at MV tips
- TDI Septal and Lateral Mitral annulus
- Color on Pulmonary veins
- PW on Pulmonary veins
- LA Volume in end-Systole
- RV Focused View in 2D
- Color on TV
- CW on TV
- RA Area and RA Volume in end systole
- TDI of lateral annulus of TV for S’
- M Mode of lateral annulus of TV for TAPSE
- RV Area in end diastole and end systole for FAC
- RV dimensions in end diastole (At Base, mid and mid annulus to apical level)
Apical Three Chamber View:
- 2D Image
- Color on LVOT and AV
- CW on AV for IVRT
- PW in LVOT
Apical Two Chamber View:
- 2D Image
- Color on MV
Subcostal View: (SC)
- Four chamber view in 2D
- Color on IAS
- PW on IAS
- IVC and Hepatic Veins in 2D and Color Doppler
- PW Doppler on Hepatic Veins
- Measure IVC Diameter in end diastole
- Measure IVC collapsibility index
- 2D image of Abdominal Aorta
- Color on Abdominal Aorta
- PW Doppler on Abdominal Aorta
Supraternal View:
- 2D Image
- Color on Ascending Aorta
- PW on Ascending Aorta
- Color on Descending Aorta
- PW on Descending Aorta
- CW on Descending aorta
3. Identification of key structures in major views:
Following images are labelled to identify key structures during study.1. Identification of Wall Segments for the assessment of wall motion abnormality:
2. Identification of Key Structures:
 |
| Parasternal Long Axis View (PLAX) Labelled |
 |
| Parasternal RV Inflow View (RVI) showing RA, RV and Tricuspid Valve |
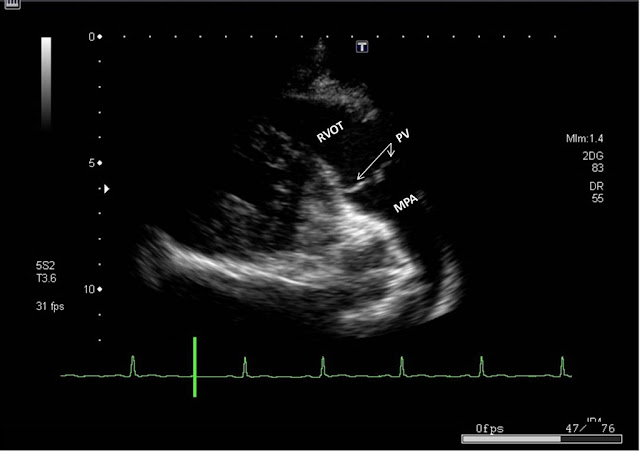 |
| Parasternal RV Outflow view showing RVOT, Main Pulmonary artery (MPA) and Pulmonary Valve |
 |
| Parasternal Short Axis View (PSAX) at the level of Aortic Valve (AV) |
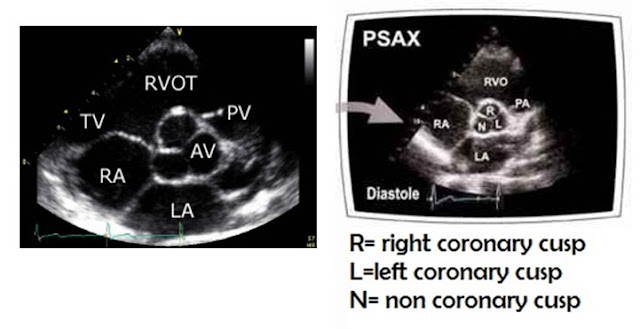 |
| Magnified view of Parasternal Short Axis View (PSAX) at the level of Aortic Valve (AV) showing three cusps of AV |
 |
| Apical Four chamber View (A4C), ATVL: Anterior TV leaflet, STVL: Septal tricuspid Valve leaflet, AMVL: Anterior Mitral valve leaflet, PMVL: Posterior Mitral valve leaflet |
 |
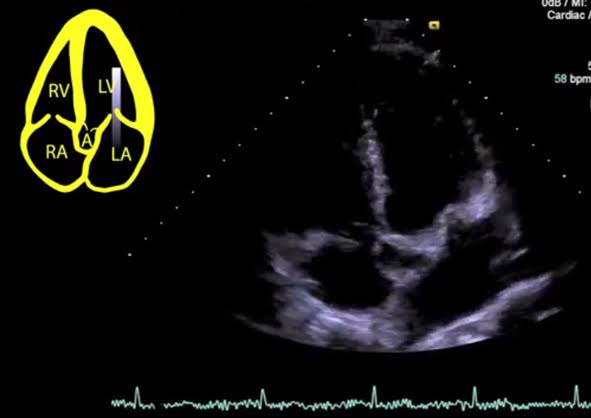
| Apical three chamber view (A3C) - labelled |
 |
| From A4C , Apical 5 chamber view is obtained by directing beam more anteriorly towards the AV which is anterior structure within the thorax |
 |
| Subcostal view - labelled |
3. Tricuspid Valve Leaflets in different Views:
 |
| Apical four chamber view showing Anterior and septal leaflets of Tricuspid valve |
 |
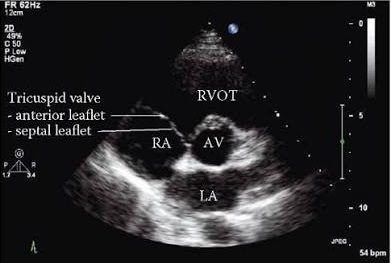
| RV Inflow showing Anterior and Posterior Tricuspid valve leaflets |
 |
| PSAX view showing Anterior and septal leaflet of Tricuspid Valve |
4. Complete Transthoracic Echocardiogram:
Now watch this complete video of a normal tranthoracic echocardiogram with all the steps performed according to protocol we have discussed and try to identify all the structures.
✅ Visit Echo MOCK Exam Section >>
✅ Visit ECHO Library to explore more resources.
HAPPY LEARNING!!! You are welcome to suggest any improvements or feedback in the comment section below.


Very helpful, thank you!
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing this brilliant presentation
ReplyDeleteThanks I'm starting this year with the vascular techniques as well, I appreciate it very much.
ReplyDeleteExcellent video presentation, thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeletevery useful tutorial ! Thank you very much for sharing it!
ReplyDeleteSo clear and helpful! i'm a regular reader of your blog
ReplyDeleteGreat blog
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDeleteExcellent knowledge, which is both excellent and crucial for everyone. I sincerely appreciate you sharing this type of information. Once more, I appreciate you sharing it. Echocardiogram in Funda Medic
ReplyDeleteYou have done good work by publishing this article here. I found this article too much informative, and also it is beneficial to enhance our knowledge for Cost of echocardiogram. Grateful to you for sharing an article like this.
ReplyDeleteA very informative blog on explaining echocardiography standard. Thank you very much for posting this blog. The cardiology hospital in Chennai treats heart attacks, heart failure, heart valve disease, arrhythmia, and high blood pressure. They are specialized training in diagnosing and treating heart-related issues.
ReplyDeleteA transoesophageal echocardiogram (TOE) is an ultrasound scan which looks at the structure and function of your heart.
ReplyDelete